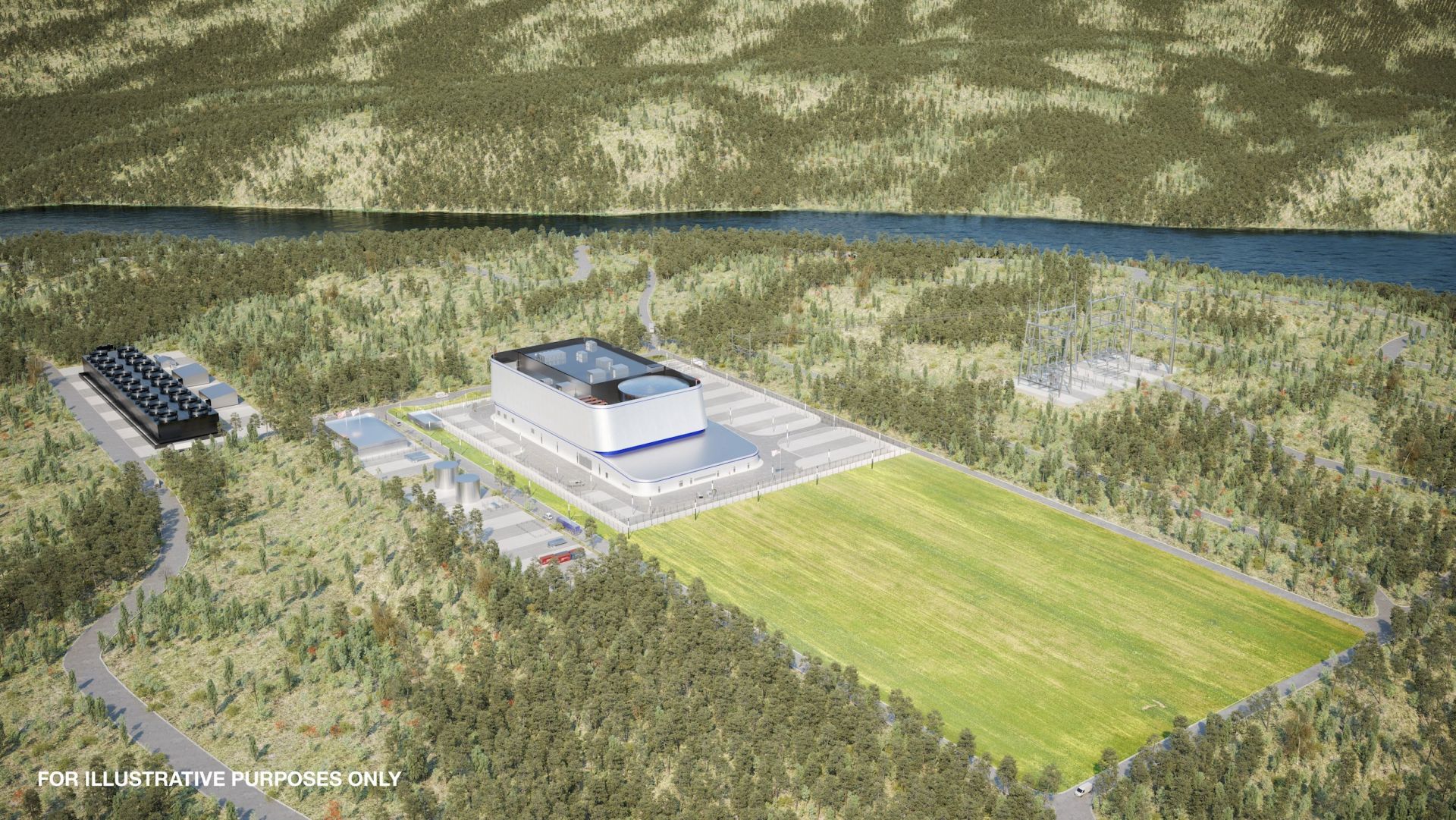
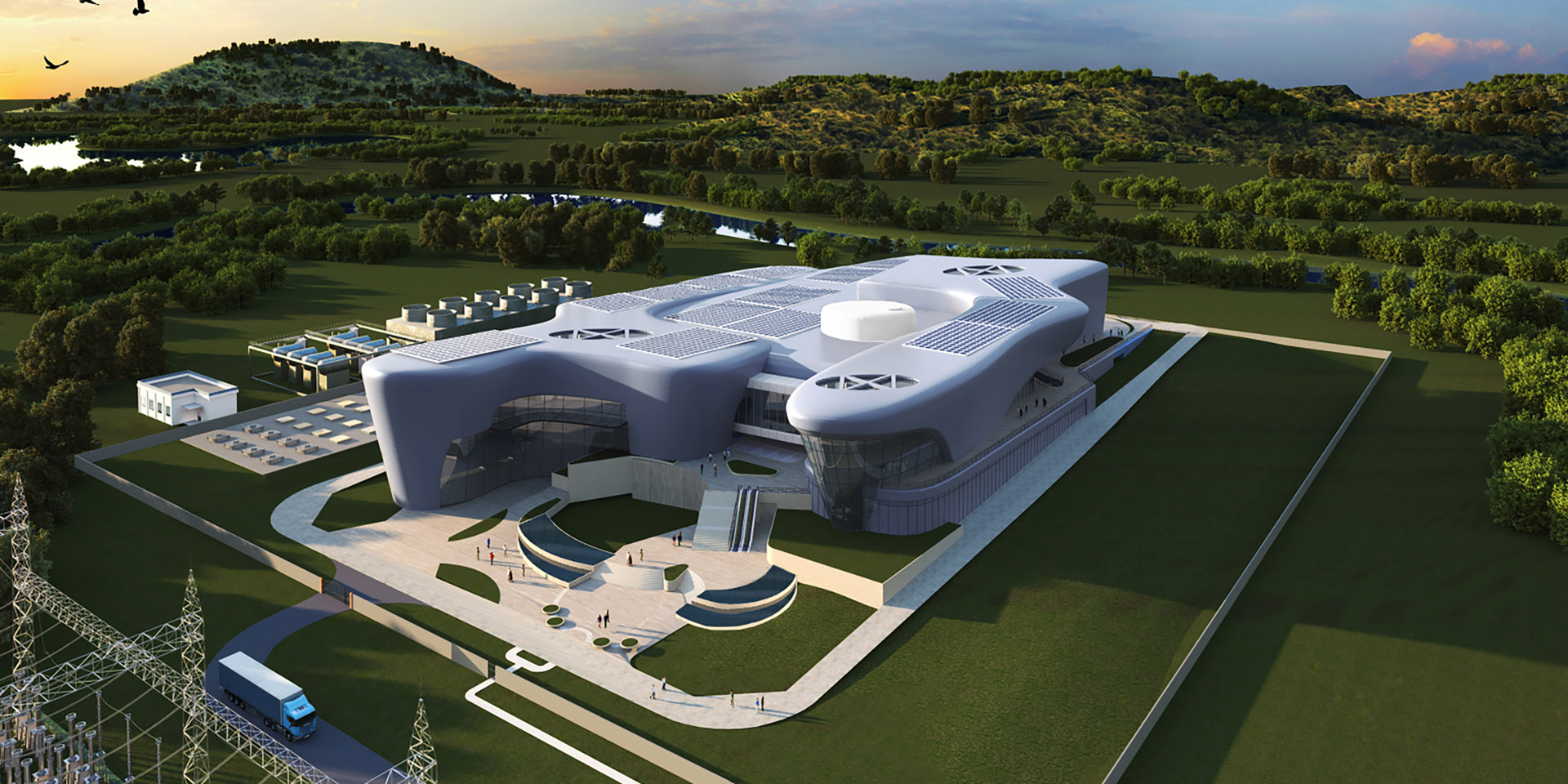
A rendering of Holtec’s SMR-160 plant. (Image: Holtec International)
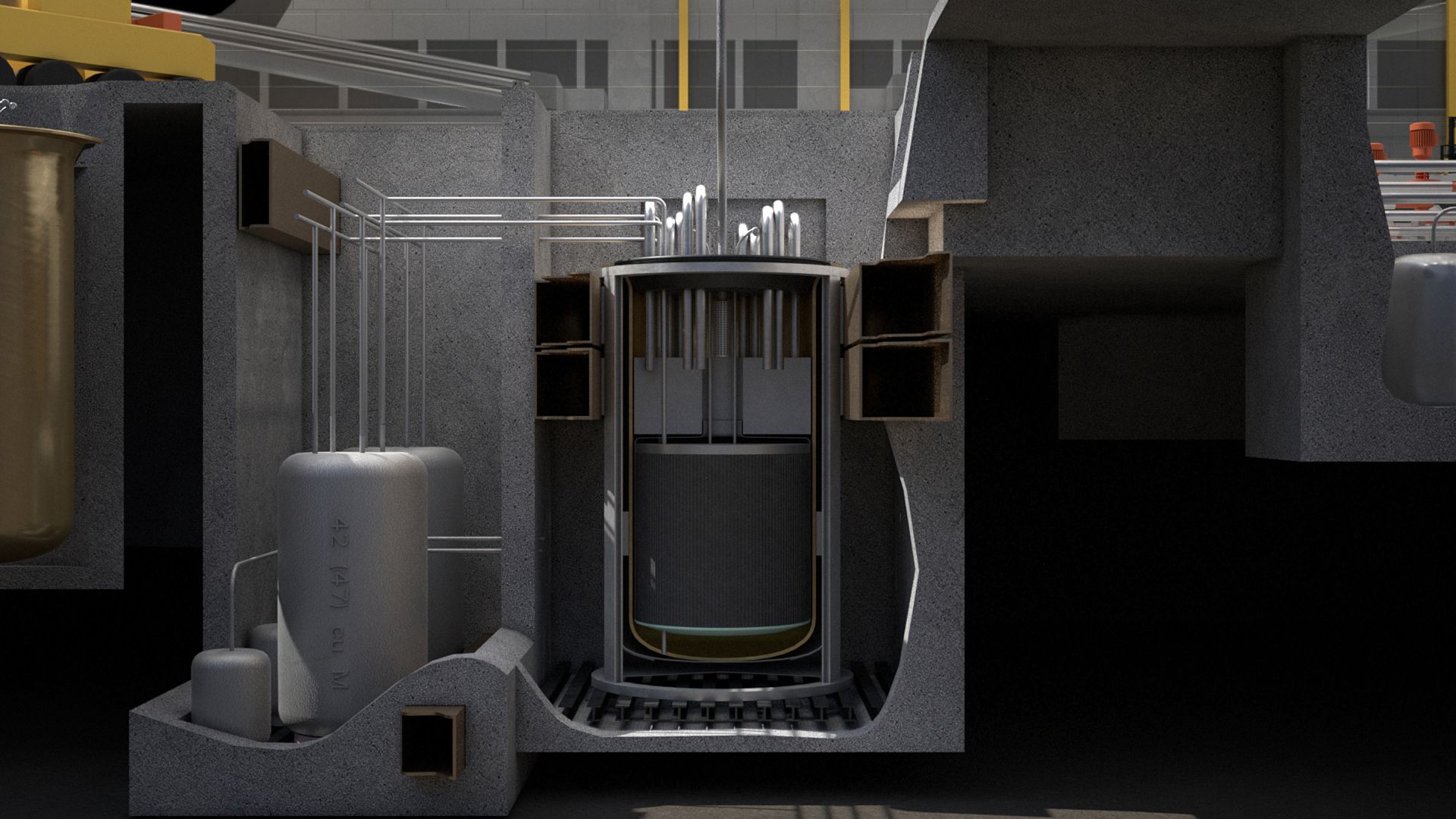
Small modular reactor developers Holtec International and GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH) are both looking to the United Kingdom as a prime location for deployment of their units—the SMR-160 and BWRX-300, respectively.
On December 19, Holtec Britain announced that it is poised to enter the United Kingdom’s generic design assessment (GDA) process for the SMR-160 early in 2023, enabling the start of construction of the first U.K. unit as soon as 2028. (The GDA, developed by the Office for Nuclear Regulation and the Environment Agency, gauges the safety, security, and environmental protection aspects of a nuclear plant design. Successfully completing the assessment culminates in a design acceptance confirmation from ONR and a statement of design acceptability from the Environment Agency.)
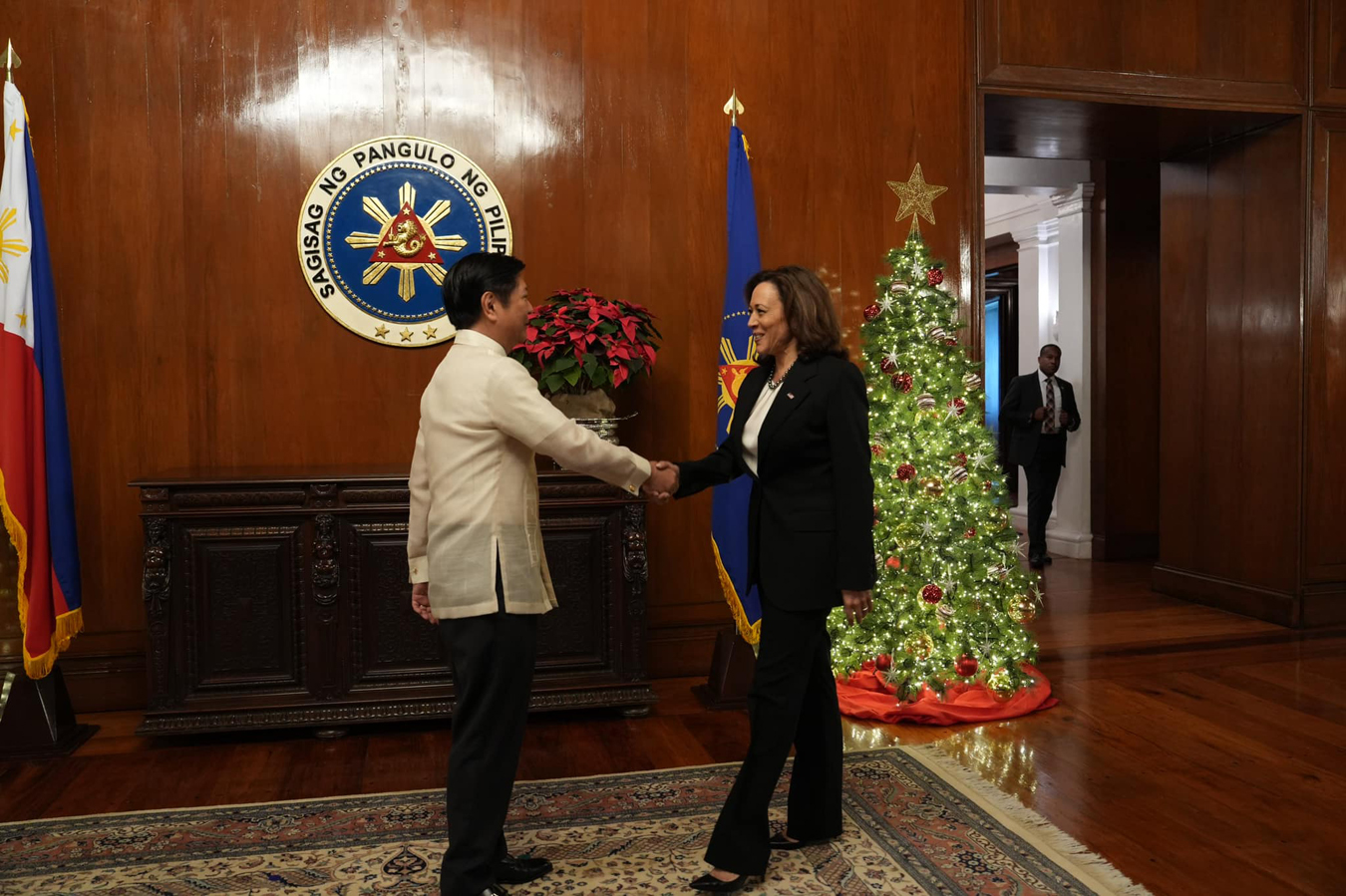
Philippine president Ferdinand R. Marcos Jr. and Vice President Harris meet in Manila on November 21. (Photo: Office of the Press Secretary, Republic of the Philippines)
During a recent weeklong trip to Southeast Asia aimed at bolstering U.S. economic and security ties in the region, Vice President Kamala Harris announced the launch of nuclear energy partnerships with Thailand and the Philippines.
Currently, neither country enjoys the benefits of nuclear power. Both rely primarily on some mix of petroleum, natural gas, and coal for their energy needs.
From left: U.S. undersecretary of state for arms control and international security Bonnie Jenkins; Japan’s state minister of economy, trade, and industry Fusae Ōta; Ghana’s deputy minister of Energy William Owuraku Aidoo; and U.S. assistant secretary for nuclear energy Kathryn Huff. (Photo: DOE Office of Nuclear Energy)
The United States and Japan have announced Winning an Edge Through Cooperation in Advanced Nuclear (WECAN)—a new agreement aimed at supporting the deployment of small modular reactors and other advanced reactor technologies in partner countries.
An artist’s rendering of Natrium. (Image: TerraPower)
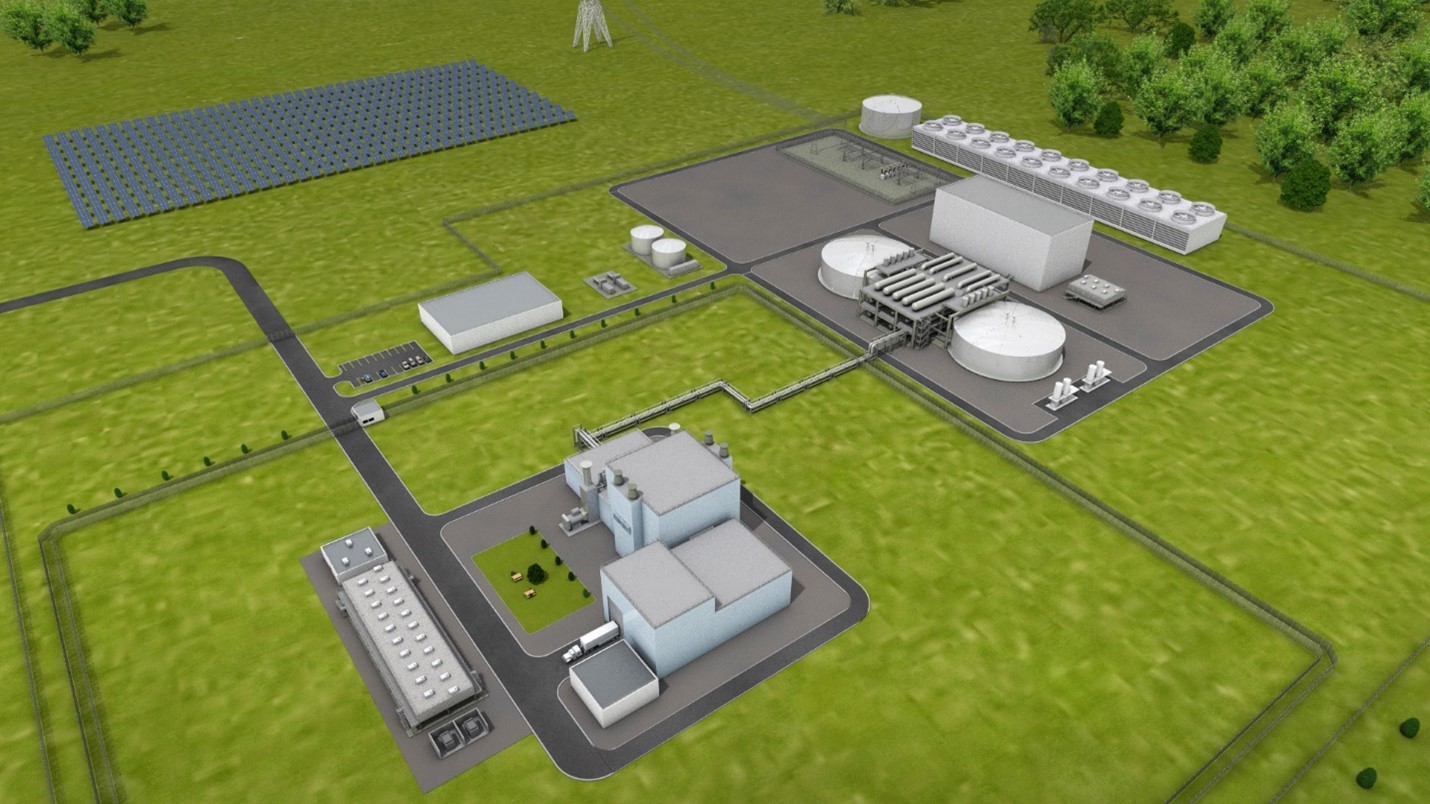
Nuclear technology firm TerraPower and utility partner PacifiCorp have launched a study to evaluate the feasibility of deploying up to five additional Natrium reactor and integrated energy storage systems in the utility’s service territory by 2035, the companies announced yesterday. (PacifiCorp’s business units—Pacific Power and Rocky Mountain Power—serve customers in California, Oregon, and Washington, and in Idaho, Utah, and Wyoming, respectively.)
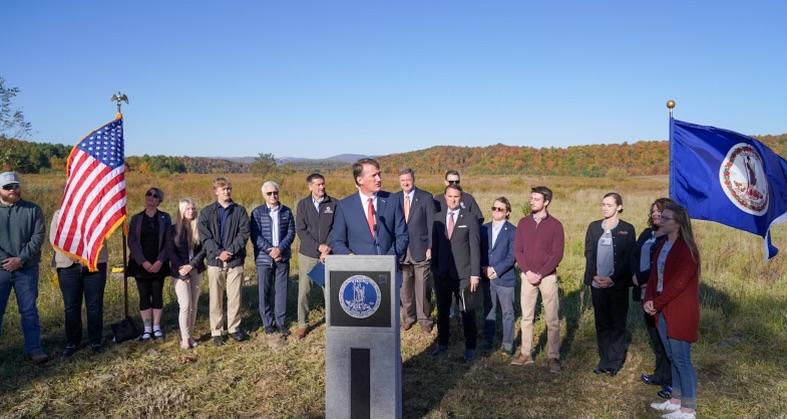
Virginia Gov. Glenn Youngkin announces a $10 million energy innovation investment in Virginia. (Photo: Christian Martinez/Office of the Governor)
Some two weeks after unveiling his state’s 2022 Energy Plan, Virginia Gov. Glenn Youngkin has announced his intention to include $10 million in the state’s next budget proposal—due in December—to create the Virginia Power Innovation Fund for research and development of nuclear, hydrogen, carbon capture and utilization, and battery storage technologies.
Artist’s rendering of the IMSR Core-Unit. (Credit: Terrestrial Energy)
In the ongoing quest to mitigate the effects of climate change, new technology can create new solutions. Even today, however, coal is still a main source of power around the globe, often out of necessity. Many coal-burning plants have already been converted for gas or biomass, but these measures alone are not nearly enough to meet net-zero carbon goals. There is a better solution, however: repowering coal plants with nuclear technology—specifically, Generation IV reactors.
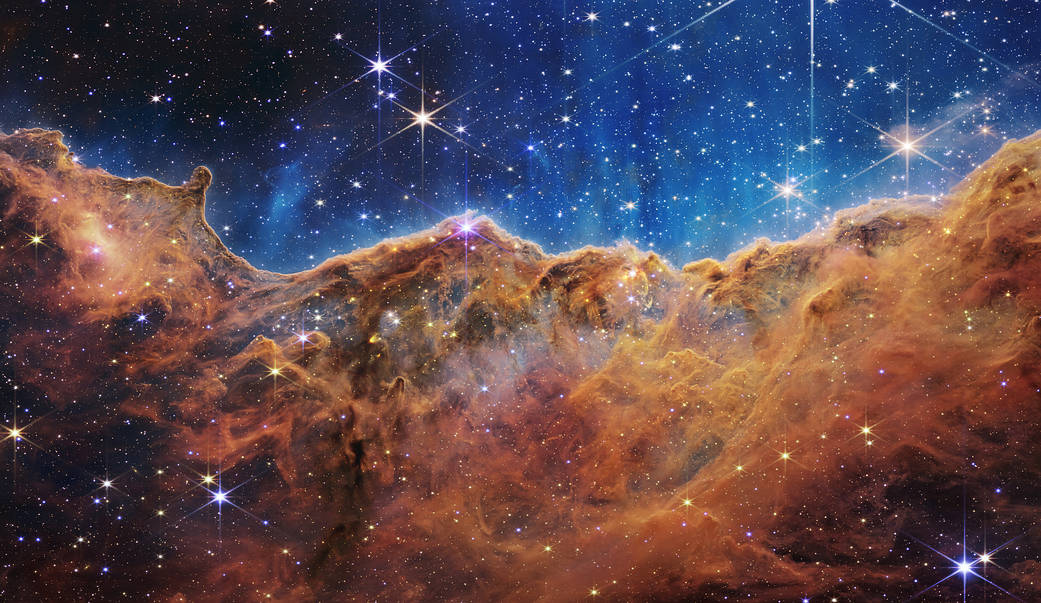
This landscape speckled with glittering stars is the edge of a nearby, young, star-forming region called NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula. Captured in infrared light by NASA’s new James Webb Space Telescope, this image reveals for the first time previously invisible areas of star birth. (Photo: NASA)
ANS’s August 4 online event “The New Space Race is Going Nuclear” featured several expert panelists who discussed the growing importance of nuclear technologies in space commercialization and exploration. Although nuclear energy has long played a role in space missions, participants discussed the latest exciting developments in the space nuclear field and presented their views on how increased application of nuclear technologies could fundamentally transform the ways in which both crewed and uncrewed space missions are carried out.
Rendering of the proposed GEH Nuclear Energy BWRX-300 SMR at the Clinch River site. (Image: GE Hitachi)
The Tennessee Valley Authority and GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH) have signed an agreement to support planning and preliminary licensing for the potential deployment of a BWRX-300 small modular reactor at the Clinch River site near Oak Ridge, Tenn., the utility’s president and chief executive officer, Jeff Lyash, announced last week.
An evolution of GEH’s 1,520-MWe Generation III+ ESBWR design, the BWRX-300 is a 300-MWe water-cooled, natural-circulation SMR with passive safety systems.








 Released this week in the lead-up to November’s COP27 event in Egypt is a report from the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe,
Released this week in the lead-up to November’s COP27 event in Egypt is a report from the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe,